This resource is hosted by the Nelson Mandela Foundation, but was compiled and authored by Padraig O’Malley. It is the product of almost two decades of research and includes analyses, chronologies, historical documents, and interviews from the apartheid and post-apartheid eras.
Home language
The most widely spoken home language in South Africa outside the TBVC is Zulu which has over 8.35-million speakers. Afrikaans comes next with 5.75-million and English fourth as the home language of 3.4-million people.
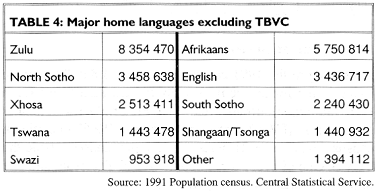
Because these rankings exclude the ethnically-based TBVC territories, they are misleading. Xhosa is spoken and has official status in Transkei and Ciskei and the same applies to Tswana in Bophuthatswana and to Venda in Venda. The combined population of Transkei and Ciskei is 4.2-million (Table 1) which, if added to 2.5-million Xhosa speakers in the rest of the country (Table 4), totals 6.7-million. This suggests that Xhosa should rank as the second most widely spoken language after Zulu. Similarly, the number of Tswana mother tongue speakers should rank alongside that of North Sotho with 2.1-million people living in Bophuthatswana and 1.4-million speakers living in the rest of the country.
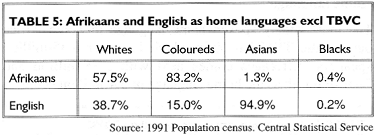
The small numbers of blacks speaking English and Afrikaans as home languages appear to support this hypothesis: